Tag: language
Why translate?
28 January 2015 | Essays, Non-fiction

Down by the sea: Herbert Lomas in Aldeburgh. – Photo: Soila Lehtonen
‘People do not read translations to encourage minor literatures but to rediscover themselves in new imaginative adventures‚’ says the poet and translator Herbert Lomas in this essay on translation (first published in Books from Finland 1/1982). ‘Translation is a thankless activity,’ he concludes – and yet ‘you have the pleasure of writing without the agony of primary invention. It’s like reading, only more so. It’s like writing, only less so.’ And how do Finnish and English differ from each other, actually?
Any writer’s likely to feel – unless he’s a star, a celebrity, a very popular and different beast – that the writer is a necessary evil in the publisher’s world, but not very necessary. How much more, then, the translator from a ‘small’ country’s language.
Why do it? The pay’s absurd, you need the time for your own writing, it’s very hard to please people, and translation is, after all, the complacent argument goes, impossible. I’m convinced by all these arguments, and really I can’t afford to go on; but I don’t regret what I’ve done and, looking back, I can find two reasons for translating Finnish writing, one personal, the other cultural. More…
Encounters with a language
12 December 2014 | Articles, Non-fiction

Mistranslation: illustration by Sminthopsis84/Wikimedia
Mother tongue: not Finnish. How do people become interested enough in the Finnish language in order to become translators? In the olden days some might have been greatly inspired by the music Sibelius (as were the eminent British translators of Finnish, David Barrett or Herbert Lomas, for example, back in the 1950s and 1960s). We asked contemporary translators to reminisce on how they in turn have become infatuated enough with Finnish to start studying and translating this small, somewhat eccentric northern language. Three translators into English, one into French, German and Latvian tell us why
Tellervo Krogerus: Sanottu. Tehty. Matti Kuusen elämä 1914–1998. [Said. Done. The life of Matti Kuusi, 1914–1998]
22 May 2014 | Mini reviews, Reviews
 Sanottu. Tehty. Matti Kuusen elämä 1914–1998
Sanottu. Tehty. Matti Kuusen elämä 1914–1998
[Said. Done. The life of Matti Kuusi, 1914–1998]
Helsinki: Siltala , 2014. 856 pp., ill .
ISBN 978-952-234-194-5
€31.50, hardback
The folklorist Matti Kuusi vied for the status of the world’s leading researcher of proverbs with the Californian scholar Archer Taylor, his work extending from the shores of the Baltic Sea to Namibia’s Ovamboland. Proverbs revealed to him the deep structures of the human mind and showed that the nations of the world possessed a basis for mutual understanding. As a young man Kuusi read Spengler and predicted the destruction of the Western world. According to his ‘Kalevalan imperialism’, the Nordic region was to be the new world power. The war brought him to his senses: he understood that patriotism was mainly a matter of bland resilience. Professor Kuusi was a rigorous scholar, but also a provocative man of ideas who showed that pop music was today’s folk poetry. That idea received a mixed reception, but nowadays his department studies both rap music and ancient folk song. This biography by Tellervo Krogerus creates a rich portrait of a complex personality.
Translated by David McDuff
Beautiful books
15 May 2014 | Letter from the Editors, Non-fiction
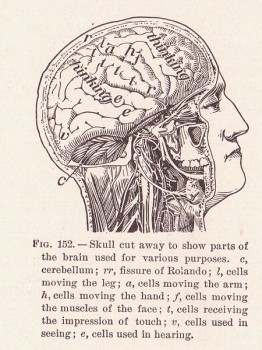
Brains at work. (Alvin Davison, ‘The Human Body and Health’, 1908) Wikimedia
A precise translation of the word non-fiction doesn’t exist in the Finnish language. Fiction is kaunokirjallisuus (a word invented by two diligent scholars, D.E.D. Europaeus and A. Varelius in mid-19th century for their Swedish-Finnish dictionary) – and a pretty word it is: kauno- is derived from the word kaunis, beautiful, beauteous. Non-fiction translates as tietokirjallisuus: literally, ‘literature of knowledge’.
Recently the status of Finnish non-fiction has been discussed in various media. Authors of non-fiction, as well as a number of readers, have been worried about diminishing sales, a decline in interest among both the general public and publishers, a lack of professional publishers’ editors. In a small-language area producing and profitable publishing ‘literature of knowledge’ is financially hard. More…
Breadcrumbs and elephants
27 March 2014 | Essays, On writing and not writing

In this series, Finnish authors ponder the pros and cons of their profession. Alexandra Salmela operates in two languages, her native Slovakian and Finnish, which has become her literary language. Adventure and torture alternate as she attempts to shape reality into writing
I had started to write before I knew how. With fat wax crayons, in big stick-letters, I scratched my stories in old diaries. There were lots of pictures. From the very beginning, I wrote both poetry and prose. At 11 I didn’t finish my great sea-adventure novel, but at 12 I was already writing my memoirs. They, too, somehow remained unfinished.
Writing is… I wanted to write fun, but in the end I’m not quite sure about that. Writing is adventure and liberation and terribly hard work. Torture of the imagination and the pale copying of real events. Reading is a way to escape reality and at the same time a route to the sources of reality. By writing, you can shape reality in your own image: it’s your own character fault if the result is ugly and depressing.
If I were to write a pink world, it would be so sugary that it would make everyone sick, me and other people. More…
Writing silence
6 June 2013 | Fiction, poetry, Reviews
In contemporary poetry the ‘lyric I’ of previous decades often hides behind language; the poem’s speaker is not the poet him/herself, narrative is not the norm. The website of a Finnish family magazine in 2007 discussed this: ‘OMG, this thing called contemporary poetry – crap!’; ‘Who knows what kind of psychopharma the writer’s on!’; ‘No meanings, just words one after the other. Why can’t people write something sensible?’ But the writer – and the reader – of contemporary poetry deliberately ventures onto the boundaries of language, and art requires readers (listeners, viewers) to make the decision of what they consider ‘sensible’. Mervi Kantokorpi explores and interprets two new collections of poetry
I read two of this spring’s new collections of poetry one after the other: Kivirivit (‘Stone lines’, Otava 2013) by Harry Salmenniemi and Pysty hiljaisuus (‘Vertical silence’, Teos 2013) by Miia Toivio. The experience was perplexing.
These two works are completely different from one another as regards their individual poetics, and yet the similarities between the themes that arise from them was arresting. Both works seem to inhabit an internal world of sorrow and depression, a world where the function of poetry is to forge and show its readers a path out of the anxiety. In their silence – and even emptiness – both collections have two faces: one lit up, the other darkened by grief. More…
Fatherlands, mother tongues?
12 April 2013 | Letter from the Editors

Patron saint of translators: St Jerome (d. 420), translating the Bible into Latin. Pieter Coecke van Aelst, ca 1530. Walters Art Museum, Baltimore. Photo: Wikipedia
Finnish is spoken mostly in Finland, whereas English is spoken everywhere. A Finnish writer, however, doesn’t necessarily write in any of Finland’s three national languages (Finnish, Swedish and Sámi).
What is a Finnish book, then – and (something of particular interest to us here at the Books from Finland offices) is it the same thing as a book from Finland? Let’s take a look at a few examples of how languages – and fatherlands – fluctuate.
Hannu Rajaniemi has Finnish as his mother tongue, but has written two sci-fi novels in English, which were published in England. A Doctor in Physics specialising in string theory, Rajaniemi works at Edinburgh University and lives in Scotland. His books have been translated into Finnish; the second one, The Fractal Prince / Fraktaaliruhtinas (2012) was in March 2013 on fifth place on the list of the best-selling books in Finland. (Here, a sample from his first book, The Quantum Thief, 2011, Gollancz.)
Emmi Itäranta, a Finn who lives in Canterbury, England, published her first novel, Teemestarin tarina (‘The tea master’s book’, Teos, 2012), in Finland. She rewrote it in English and it will be published as Memory of Water in England, the United States and Australia (HarperCollins Voyager) in 2014. Translations into six other languages will follow. More…
Love me tender… in Latin
12 April 2013 | This 'n' that

Latin Bible, 1407. Malmesbury Abbey, Wiltshire, UK. Photo: Arpingstone, Wikipedia
Nuntii Latini, conspectus rerum internationalium hebdomadalis, est programma Radiophoniae Finnicae Generalis in terrarum orbe unicum.
Nuntii Latini is a five-minute radio programme broadcast every Friday by the Finnish Broadcasting Company, YLE. It is the only regular news programme in Latin in the world, and has been on the air since 1989. (Not even Vatican Radio broadcasts news.)
Professor Tuomo Pekkanen from Jyväskylä University and Reijo Pitkäranta are the founding fathers of the programme, and they are helped by some other friends of Latin.
In a report on 8 April The New York Times wrote that even Elvis Presley has inspired the friends of the dead language: Jukka Ammondt, a Finnish university lecturer in English and German, began singing Elvis songs in Latin a couple of decades ago, and occasionally still does. Love Me Tender: Tenere Me Ama.
John Tagliabue describes in his article how Leah Whittington, an English professor at Harvard, ‘catches the news bulletins on her iPod while strolling to classes.’ Whittington says: ‘I’m often struck when I’m listening how well structured they are, how idiomatic, how precise the vocabulary is.’
The editors don’t invent new words, they look for new expressions using existing Latin vocabulary. A golf course, for example, is campus pilamallei.
Maailman paras maa [The best country in the world]
14 March 2013 | Mini reviews, Reviews
 Maailman paras maa
Maailman paras maa
[The best country in the world]
Toim. [Ed. by] Anu Koivunen
Helsinki: Suomalaisen Kirjallisuuden Seura, 2012. 255 p., ill.
ISBN 978-952-222-347-0
€ 37, paperback
In this book twelve writers, representing various fields of research, ponder Finland and Finnishness from the viewpoint of history, ethnology, society, culture and economics. Finland-Swedishness and the relationship between Finns and Russians, the need of Finns to defend their participation in the Second World War in alliance with Germany as a ‘separate war’, and the nostalgia related to lost Karelia. The articles deal with Finland facing economic challenges, attitudes towards foreign beggars and self-critical Finnish opinion pieces. They also take a look at Finnish man as portrayed in the classic novel Seitsemän veljestä (‘The seven brothers’, 1870, by Aleksis Kivi) and in a recent prize-winning film about men talking in the sauna about their feelings, and discuss the relationship of the two national languages, Finnish and Swedish. Well-written and original articles question truisms and challenge the reader contemplate his or her own relationship with Finnishness.
On the meaning of translation
28 February 2013 | This 'n' that
 Translations of Finnish literature into English are booming, according to a new website set up by the Finnish-English Literature Translation Co-operative, or FELT.
Translations of Finnish literature into English are booming, according to a new website set up by the Finnish-English Literature Translation Co-operative, or FELT.
Or at least there is a tiny boom, as translator Lola Rogers puts it in her contribution to ‘Reflections’ on the FELT website.
Whereas less than 20 translations were published between 1992 and 2002, the number of translations published in the decade from 2002 was more than 34.The reason, according to FELT, is the new availability of qualified literary translators, whom the new website has been created to represent; each of them (David Hackston, Emily Jeremiah, Kristian London, Lola Rogers, Owen Witesman) now have two or more published Finnish works of fiction under their belts.
A significant factor has been the training events organised by FILI, Finnish Literature Exchange, publisher of this magazine – and, we might dare to say, Books from Finland itself, which offers translators a forum (as well as payment) for translations of extracts from interesting or significant new work.
The FELT website is worth a visit by anyone with an interest in Finnish literature – or translation. As well as details of published and forthcoming work, there is a collection of essays on the art of translating particular works, from Kristina Carlson (also ex-Editor-in-Chief of Books from Finland) to the novelist Asko Sahlberg and the modernist poet Eeva-Liisa Manner.
Kalevala maailmalla. Kalevalan käännösten kulttuurihistoria [The Kalevala in the world. A cultural history of Kalevala translations]
15 November 2012 | Mini reviews, Reviews
 Kalevala maailmalla. Kalevalan käännösten kulttuurihistoria
Kalevala maailmalla. Kalevalan käännösten kulttuurihistoria
[The Kalevala in the world. A cultural history of Kalevala translations]
Toim. [Ed. by]: Petja Aarnipuu
Helsinki: Finnish Literature Society and Kalevala Society, 2012. 396 p., ill.
ISBN 978-952-222-372-2
€48, paperback
The Kalevala, based on the folk poetry collected by Elias Lönnrot, is Finland’s national epic. It first appeared in 1835, with a revised edition in 1849. The work has been published in more than 200 different versions in 60 languages, including prose translations, abridgements and adaptations. In this study, scholars and authors examine the Kalevala’s conquest of the world from many angles, ranging from Finland’s neighbouring regions, the epic traditions of Africa, the application of the epic to economic life, and the history of the work’s translation into the major languages of the world. The articles explore the linguistic, stylistic and cultural problems involved in translating the work and the experiences of some of the translators – for example, those who put the Kalevala into Iroquois. They also look at the motives behind the translations, and why in some languages there are several different versions. The book offers a varied and fascinating perspective on the epic’s cultural history.
Translated by David McDuff
See the big picture?
9 November 2012 | Extracts, Non-fiction

Details from the cover, graphic design: Työnalle / Taru Staudinger
In his new book Miksi Suomi on Suomi (‘Why Finland is Finland’, Teos, 2012) writer Tommi Uschanov asks whether there is really anything that makes Finland different from other countries. He discovers that the features that nations themselves think distinguish them from other nations are often the same ones that the other nations consider typical of themselves…. In Finland’s case, though, there does seem to be something that genuinely sets it apart: language. In these extracts Uschanov takes a look at the way Finns express themselves verbally – or don’t
Is there actually anything Finnish about Finland?
My own thoughts on this matter have been significantly influenced by the Norwegian social scientist Anders Johansen and his article ‘Soul for Sale’ (1994). In it, he examines the attempts associated with the Lillehammer Winter Olympics to create an ‘image of Norway’ fit for international consumption. Johansen concluded at the time, almost twenty years ago, that there really isn’t anything particularly Norwegian about contemporary Norwegian culture.
There are certainly many things that are characteristic of Norway, but the same things are as characteristic of prosperous contemporary western countries in general. ‘According to Johansen, ‘Norwegianness’ often connotes things that are marks not of Norwegianness but of modernity. ‘Typically Norwegian’ cultural elements originate outside Norway, from many different places. The kind of Norwegian culture which is not to be found anywhere else is confined to folk music, traditional foods and national costumes. And for ordinary Norwegians they are deadly boring, without any living link to everyday life. More…
Pen to paper
25 October 2012 | Articles, Non-fiction
Writing is ancient: the act of taking a stylus, a quill or a pen into one’s hand still feels powerful. Will we find a way of scrawling in space, to mark our individuality, wonders Teemu Manninen
It was my vacation, and I wanted to catch up on some fun writing projects, but because I didn’t want to depend on my devices (would we have wifi? would the batteries last?) or carry around too much extra stuff I bought a red notebook and wrote in black ink on white paper while sitting in cafes and restaurants with my wife.
Writing by hand got me – surprise – to thinking about handwriting in general. Etymologically, ‘writing’, from Old English writan, means scratching, drawing, tearing. In the original Hebrew, God does not simply fashion humans out of clay, he writes them: his word is his image, giving life to the letter of his meaning, the human being.
Writing is violence. It brings about vivid change in the matter of the world: in the age of clay tablets, the stylus was a carving instrument. During the age of ink, cutting the tip of the quill was, if we believe the early Renaissance manuals of handwriting, as precise and violent an act as cutting someone’s head off. More…
Do you speak my language?
23 August 2012 | Articles, Non-fiction
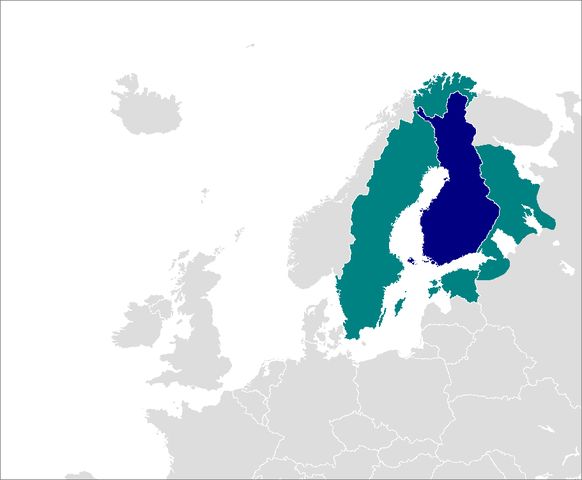
Finnish spoken outside Finland: Sweden (west), Estonia (south), Karelia/Russia (east), Norway (north). Illustration: Zakuragi/Wikipedia
Finland has two official languages, Finnish and Swedish. Approximately five per cent of the population (290,000 Finns) speak Swedish as their native language. All Finns learn both languages at school, and students in higher education must prove they have an adequate knowledge of the other mother tongue. But how do native speakers of Finnish cope with what is, for many of them, a minority language that they will never need or even wish to use? We take a look at bilingual issues – and a new book devoted to them
‘In many parts of the world, language can be a fiery and divisive issue, one that pits the powerless against the powerful, the small against the big. The Basques battle the Spanish. The Flemish tussle with the Walloons. The Québécois scuffle with the rest of Canada.’
That is how Lizette Alvarez illustrated her theme in her article ‘Finland Makes Its Swedes Feel at Home’, published in the New York Times in 2005.
In Finland, language has been a fiery issue at times, though things have cooled down a bit since the early 20th century. The use of Finnish as a written language dates back to the 16th century, but the territory of Finland was part of the Swedish Empire until 1809. Swedish was spoken by the nobility as well as most of the peasant class – the mechanism of the state did not serve Finnish-speaking peasants or other segments of the population in Finnish. More…
Indifference under the axe
9 March 2012 | Essays, Non-fiction

In the forest: an illustration by Leena Krohn for her book, Sfinksi vai robotti (Sphinx or robot, 1999)
The original virtual reality resides within ourselves, in our brains; the virtual reality of the Internet is but a simulation. In this essay, Leena Krohn takes a look at the ‘shared dreams’ of literature – a virtual, open cosmos, accessible to anyone, without a password
How can we see what does not yet exist? Literature – specifically the genre termed science fiction or fantasy literature, or sometimes magic realism – is a tool we can use to disperse or make holes in the mists that obscure our vision of the future.
A book is a harbinger of things to come. Sometimes it predicts future events; even more often it serves as a warning. Many of the direst visions of science fiction have already come true. Big Brother and the Ministry of Truth are watching over even greater territories than in Orwell’s Oceania of 1984. More…
