Author: The Editors
Panem et circenses?
2 February 2012 | This 'n' that
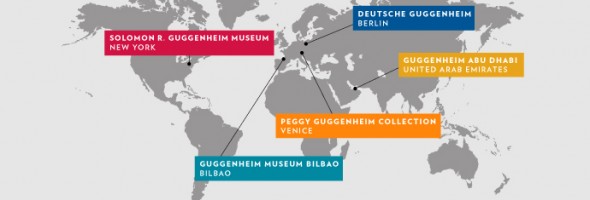
The Guggenheim Foundation's global network of museums
What does Helsinki need? Bread and circuses, yes, but at what cost the latter?
In January – after a study that cost the Finns a couple of million euros – the Salomon R. Guggenheim Foundation (est. 1937) indicated that it was favourably inclined toward the construction of a new art museum, bearing its name, in Helsinki. The leaders of Helsinki city council are aiming to make a positive decision as soon as possible.
The cost of the building, whose site adjoins the Presidential Palace in central Helsinki, is estimated at 130–140 million euros, with design costs of about 11 million euros. Unlike in the case of Berlin, no existing building is considered suitable; instead, an architectural dream must be realised, with plenty of wow-factor.
Its mere maintenance costs will be around 14.5 million euros a year. It has been estimated that the Helsinki Guggenheim’s income could be 7.7 million a year. In addition, a 20-year Guggenheim licence costs 24.6 million euros.
The project has provoked widely differing reactions. Proponents of the project believe that the Guggenheim brand would bring thousands of new visitors to Helsinki and that half a million people would visit it each year. Opponents doubt this, speak of a ‘Guggenburger’ franchising concept and of the fact that not even the existing art museums of Helsinki are particularly crowded.
The odd thing is, however, that the basic demographic differences between Helsinki and, say, Bilbao – where the Guggenheim museum has been a big success – are constantly ignored in the discussions: the population of Spain is almost 50 million and another 50 million visitors go there every year, while the corresponding figures for this most northerly part of Europe are five million inhabitants and visitors.
In Bilbao, moreover, there was no museum of contemporary art before the advent of the Guggenheim; Helsinki, on the other hand, opened Kiasma, a new museum of contemporary art (165,000 visitors in 2010) in 1998 and the neighbouring city of Espoo its Emma museum of modern art (82,000 visitors in 2010) in 2006.
Economic prospects on any level now offer little hope. The Finnish government, in the shape of the ministry of culture, has just cut grants to state-aided museums by three million euros – the Museum of Cultures in Helsinki, for example, is closing its doors, and some 40 of the museum staff elsewhere will be sacked. The government is not promising any money to the Guggenheim.
How, then, to fund an annual deficit of 7 million euros? Finland does not have a great supply of art-minded millionaire sponsors, and no one has so far made any concrete offers on how to fund this project.
The Guggenheim Foundation itself is not taking any financial risks with this project. Neither has it announced in any detail what sort of art will feature in the museum’s temporary exhibitions.
People who live in the city are more preoccupied with, for example, the shortcomings of the health services: there are waiting lists for everything, often of many weeks, and the old university children’s hospital has outgrown its present space. There are cuts and shrinkages yet to come in the spending structure of the country as a whole and of Helsinki – civil servants themselves estimate that the city’s budget is not sufficient to cover even the upkeep of basic services.
To judge by the public debate, the deep ranks of Helsinki taxpayers do not want a new monument, one for which it will be necessary to pay – in addition to maintenance – more than a million euros a year to an American brand for the mere use of its name, for more than 20 years.
Do the people of Helsinki wish to begin to pay additional taxes for the revival, yet again, of the age-old dream of guaranteeing Finland ‘a place on the world map’, in a situation where economic difficulties are a matter of everyday life for increasing numbers of them? (We believe, incidentally, that Finland already has an appropriate place on the world map.) Will their opinion be asked, or heard?
A Finnish comics award
2 February 2012 | In the news

Kaisa Leka
Suomen sarjakuvaseura (The Finnish Comics Society) has awarded its Puupäähattu Award 2012 to the graphic artist and illustrator Kaisa Leka.
The prize is not money but a honorary hat, and is named after a classic Finnish cartoon character, Pekka Puupää (‘Pete Blockhead’), created by Ola Fogelberg and his daughter Toto. The Puupää comic books were published between 1925 and 1975, and some of the stories were made into film.
Leka describes herself as a mouse named Kaisa. Both of her legs have been replaced with steel prostheses, and she has featured disability in her comics book, for example in I Am Not These Feet.
Artificial limbs haven’t stopped her from cycling, for example, from Finland to Nice in France; she has described this tour in her book entitled Tour d’Europe.

The award: Puupäähattu (‘Blockhead hat’)
(See a video of Kaisa cycling, by Lina Jelanski.)
Too much, too soon?
20 January 2012 | This 'n' that
 Candace Bushnell’s Summer & the City (about Carrie Bradshaw’s first years in NYC, published last year) is categorised among books for children and young people on the Finnish best-sellers’ list. The Finnish translation occupied the eighth place in December.
Candace Bushnell’s Summer & the City (about Carrie Bradshaw’s first years in NYC, published last year) is categorised among books for children and young people on the Finnish best-sellers’ list. The Finnish translation occupied the eighth place in December.
But hang on, wasn’t this Carrie in the fantastically famous HBO television adaptation of Bushnell’s novel Sex and the City very much in her thirties, as were her three best friends – all with, yes, quite active ‘adult’ sex lives…? In Finland the series had a rather silly title, Sinkkuelämää, ‘Single life’.
Well, of course it would be foolish not to continue the fantasticaly famous money-spinning saga, so Bushnell has gone back in time, first to Carrie’s school years in small-town America in The Carrie Diaries (2010), then to her first years in NYC in Summer & the City (2011) – and HarperCollins has pigeonholed them among its ‘teen books’.
Confusingly, the Finnish titles of these two books also contain the word referring to the television series: Sinkkuelämää – Carrien nuoruusvuodet and Sinkkuelämää – Ensimmäinen kesä New Yorkissa. As the Finnish publisher Tammi has attached TV title to them, the customer assumes these are books for ‘adults’ – as indeed was the original Sex and the City.
This makes one wonder what exactly ‘books for young people’ are. The main characters are teens themselves? If Bushnell goes still further back in time, we shall be reading about naughty Li´l Carrie hitting another toddler on the head with her doll, in a board book.
Helsinki: World Design Capital 2012
13 January 2012 | This 'n' that

Swimming in the rain: winter joys of Helsinki. Photograph: Valtteri Hirvonen – Eriksson & Co.
After Turin (Italy, 2008) and Seoul (Republic of Korea, 2010), 2012 Helsinki is the third World Design Capital, selected in 2009 by the International Council of Societies of Industrial Design (ICSID).
Helsinki was considered to be a city where ‘design has for decades been a pivotal enabler to building an open city’.
The theme is ‘Open Helsinki – Embedding Design in Life‘. The idea is to improve the everyday life and environment of the citizens and the development of both public services and private enterprises.
In addition to Helsinki, the realisation of the Design Capital year will be carried out by four other cities: neighbouring Espoo, Vantaa and Kauniainen as well as Lahti (some hundred kilometres north of the capital). The Finnish government, two ministries, 21 commercial companies and some universities will co-operate in this project, which has a budget of 16 million euros (2010–2013).
The programme includes some 300 different events, half of them development projects, themed ‘The changing city’ or ‘New solutions’; the other half consists of various exhibitions and encounters for the citizens of Helsinki, tourists and design people.
The ultimate goal of this all is said to be ‘permanent change’. Whatever that really means – good luck!
However, as writer and design critic Kaj Kalin noted in a review in Helsingin Sanomat newspaper (30 December), Finland is full of well-educated designers, but lacks both investment money prepared to take risks and working industry: soon all production will have moved to cheaper countries – and nobody will be able to produce anything. New Finnish design, Kalin argues, mostly approximates merely to ‘a show parade of models and prototypes’.
Christmas best-sellers in Finnish fiction
13 January 2012 | In the news

Rosa Liksom. Photo: Pekka Mustonen
Most new Finnish books are printed and sold in the autumn, and sales pick up considerably in December. The number one on the December list link: in Finnish only) of best-selling fiction titles in Finland, compiled by the Finnish Booksellers’ Association, is the Finlandia Fiction Prize-winning novel Hytti nro 6 (‘Compartment number 6’, WSOY, 2011) by Rosa Liksom (this is her homepage, also in English).
The Finlandia winner was announced on 1 December, upon which the book shot – from nowhere – to the top of the list.
Laila Hirvisaari’s historical novel, Minä Katariina (‘I, Catherine’, Otava), climbed up from the third place to the second. Number three was a newcomer, a tragic love story entitled Kätilö (‘The midwife’, WSOY), by Katja Kettu, set in the last phase of the Finnish Continuation War (1941–1944).
Jari Tervo’s Layla (WSOY) was in fourth place, while November’s number one, Ilkka Remes’s thriller Teräsleijona (‘Steel lion’, WSOY), came fifth.
In November Tuomas Kyrö occupied both the fourth and the tenth place with his novels Kerjäläinen ja jänis (‘The beggar and the hare’, Siltala – a pastiche-style story inspired by Jäniksen vuosi / The Year of the Hare by Arto Paasilinna, 1975) and Mielensäpahoittaja (‘Taking offence’, WSOY, 2010). In December they were numbers six and seven, in reverse order.
Away with darkness
28 December 2011 | This 'n' that

Helsinki Cathedral, lit by Martin Kuhn. Photo: Ralph Larmann
Helsinki is about to celebrate its third Season of Light. A team of designers and artists have created a series of works that will transform the urban milieu and buildings into ‘an experience for the senses and emotions’ in early January (31st December to 9 January).
For example, Helsinki Cathedral will be illuminated by light artist Mikki Kunttu, accompanied by a special sound environment. The light installation will run every day from 5 pm to 11 pm.
The German lighting designer Martin Kuhn will create an installation around Unioninkatu street, using LED technology. It will run from 6 pm to 10 pm.
Take a look at the programme – there are also photo and video samples from the previous Seasons of Light – here.
Who knows whether Helsinki will see any snow at New Year either (Christmas was black this time); nevertheless, these colours will brighten up the darkest hours in the city.
And hey, the winter solstice is already behind us, there is going to be more and more light each day!
A new publishing company – and old
23 December 2011 | In the news
In the early months of 2012 Finland’s two old and time-honoured Swedish-language publishers, Schildts and Söderströms, will merge.
Söderströms will buy Schildts, whose owners (two non-profit associations, Svenska folkskolans vänner and Finlands svenska lärarförbund) will acquire a nearly 20 per cent share in the new company. The largest share in Schildts & Söderströms will be held by the art association Konstsamfundet (24 per cent), while the company’s third major owner will be Svenska Litteratursällskapet i Finland (15 per cent).
Both publishers have been operating with a loss in turnover of approximately half a million euros, though at the same time investment capital has brought them almost the same amount. Textbook publishing has been profitable for both, while general literature has been published at a loss.
With a turnover of slightly over six million euros, the new Schildts & Söderströms will employ a workforce of nearly 50.
 Holger Schildt founded the Finnish-Swedish publishing house of Schildts in 1913. Its most internationally famous and best-selling fiction writer is the mother of the Moomins, Tove Jansson (1914–2001). Edith Södergran, Runar Schildt, Bo Carpelan and Robert Åsbacka are, for example, Schildts’ authors.
Holger Schildt founded the Finnish-Swedish publishing house of Schildts in 1913. Its most internationally famous and best-selling fiction writer is the mother of the Moomins, Tove Jansson (1914–2001). Edith Södergran, Runar Schildt, Bo Carpelan and Robert Åsbacka are, for example, Schildts’ authors.
 Werner Söderström founded the company that bears his name in 1878. Now known as WSOY, it originally published both Finnish and Swedish-language literature; the firm of Söderström & Co. was founded in 1891 for the exclusive publishing of Swedish-language literature. Söderström’s authors have included Gunnar Björling, Jörn Donner, Monika Fagerholm and Kjell Westö, among others.
Werner Söderström founded the company that bears his name in 1878. Now known as WSOY, it originally published both Finnish and Swedish-language literature; the firm of Söderström & Co. was founded in 1891 for the exclusive publishing of Swedish-language literature. Söderström’s authors have included Gunnar Björling, Jörn Donner, Monika Fagerholm and Kjell Westö, among others.
It is thought that the merger may lead to a reduction in the number of fiction and poetry titles published – but there are also hopes that there may be an improvement in their quality.
What Finland read in November
16 December 2011 | In the news
 The latest thriller, Teräsleijona (‘Steel lion’, WSOY), by Ilkka Remes (his 15th) was at the top of the November list of best-selling fiction titles in Finland, compiled by the Finnish Booksellers’ Association.
The latest thriller, Teräsleijona (‘Steel lion’, WSOY), by Ilkka Remes (his 15th) was at the top of the November list of best-selling fiction titles in Finland, compiled by the Finnish Booksellers’ Association.
The second place was occupied by Jari Tervo’s Layla, the third by Minä Katariina (‘I, Catherine’, Otava), a Finlandia Prize -listed historical novel by Laila Hirvisaari. Tuomas Kyrö occupied both the fourth and the tenth place with his novels Kerjäläinen ja jänis (‘The beggar and the hare’, Siltala – a pastiche-style story inspired by Jäniksen vuosi / The Year of the Hare by Arto Paasilinna) and Mielensäpahoittaja (‘Taking offence’, WSOY). Strangely, we think, the Finlandia-winning novel by Rosa Liksom, Hytti no 6 (‘Compartment no 6’, WSOY), was not yet on the list – the day of the awarding was 1 December.
The best-selling list of translated fiction didn’t contain any surprises – Liza Marklund, Jens Lapidus, Paulo Coelho, Henning Mankell, Stephen King – except perhaps for the tenth book, a selection of stories entitled Hyvää joulua, Jeeves! (‘Happy Christmas, Jeeves!’, Teos), by good old P.G. Wodehouse: some of the stories have not been translated into Finnish earlier, hence the delight of local Wodehouse fans.
Among the best-selling books for children and young people were just two foreign names (Thorbjörn Egner, Lisa Jane Smith) and the three at the top were works by very well-known authors: Aino Havukainen & Sami Toivonen, Sinikka Nopola & Tiina Nopola and Mauri Kunnas. (The list is available, in Finnish, here.)
The life and deeds of the late Steve Jobs interested a lot of readers, in Finland as elsewhere, and Walter Isaacson’s translated biography topped the non-fiction list.
A musical advent calendar
9 December 2011 | This 'n' that
The Finnish Broadcasting Company has delved into its vast archives, and its website, YLE Areena, is throughout December featuring a series of musical numbers, many with reference to Christmas, sung or played Finnish singers and musicians. These inserts are being broadcast on each day, from 1 to 24 December, and they can be listened to via the Internet (although be warned, the information is given in Finnish only).
Among the Finnish composers are, among others, Oskar Merikanto (1868–1924), Erkki Melartin (1875–1937), Toivo Kuula (1883–1918) and Jean Sibelius. The sopranos Irma Urrila and Helena Juntunen are presented, singing Mozart and Gounoud respectively.
For example: on 6 December, the Finland’s Independence Day, one of the three inserts is a piano piece, entitled Pankakoski, by composer Heino Kaski (who died a day earlier than Sibelius, in September 1957), played by Juhani Lagerspetz (1995). The other two are Andante Festivo (1922), a work originally composed for a string quartet, by Jean Sibelius, played by the Radio Symphony Orchestra (1995) and a song from the 1970s opera Punainen viiva (‘The red line’) by Aulis Sallinen, sung by Matti Salminen (1984).
Fifteen more days to go…

Dolce et espressivo: Violin concerto by Sibelius, 1st movement (1905). Photo: Wikimedia
A crafty Christmas
9 December 2011 | This 'n' that

Advent calendar: make one yourself! Illustration: Virpi Penna
December: the street decorations, which have been up for a month, are beginning to look a little tawdry; the office party season is in full swing and most people are beginning to feel a little the worse for wear; there are only – let’s not count them, but far too few, shopping days left till Christmas.
Festive stress has already set in, and we’re not even halfway through the month.
That’s the scene in London, at least.
In Finland, Christmas and the weeks leading up to it are a much more muted, not to say calmer, affair. The customary greeting at this time of year is ‘rauhallisia joulunalusviikkoja’ – ‘peaceful before-Christmas weeks’ (well, who isn’t afraid of Xmas panic…) and Christmas itself has a quiet, candle-lit, somehow pious quality (even for non-believers).
The tone is set by the announcement of the Christmas peace from the city of Turku at noon on Christmas Eve, and many people still begin their celebrations with a visit to the graveyard to set a lighted candle on the graves of nearest and dearest before proceeding to the festivities: the traditional Christmas dinner (with its centrepiece of ham, not turkey), followed by a visit by Father Christmas, preferably in person.
In the harsh weather and short daylight hours of this time of year so far north, staying in has a lot to recommend it, and making things at home in preparation for Christmas has always been a popular pastime – with children in particular. This year the Thisisfinland website together with Tammi publishers, in conjunction with the writer Mysi Lahtinen and the children’s illustrator Virpi Penna, has produced an online advent calendar with a crafts project for each day up to Christmas Eve.
Whether it’s making a snowflake window from cut paper, simply painting birch-twigs white or, if the climate permits, celebrating Finland’s Independence Day (6 December) by making a lantern out of snow and a candle, these are projects that can be tackled by the young, and the young at heart, of any age.
While Joulupukki may feel slightly stressed (but with him, of course, it’s an occupational hazard), we wish you a peaceful pre-Christmas fortnight!
Finlandia Junior Prize 2011
7 December 2011 | In the news
 The musician Paula Vesala has chosen, from a shortlist of six, a book for young people by the poet Vilja-Tuulia Huotarinen, Valoa valoa valoa (‘Light light light’, Karisto). The story, which is set at the time of the Chernobyl nuclear power station disaster, poetically describes the passion and pain of first love, longing for mother and death.
The musician Paula Vesala has chosen, from a shortlist of six, a book for young people by the poet Vilja-Tuulia Huotarinen, Valoa valoa valoa (‘Light light light’, Karisto). The story, which is set at the time of the Chernobyl nuclear power station disaster, poetically describes the passion and pain of first love, longing for mother and death.
‘Not just what is told, but how it is told. The rythm and timbre of Vilja-Tuulia Huotarinen’s language are immensely beautiful. Her phrases do not exist merely to tell the story, but live like poetry or song. Valoa valoa valoa does not incline toward young people from the world of adults; rather, its voice comes, direct and living, from painful, confusing, complex youth, in which young people should really be protected from adults and their blindness. I would have liked to read this book when I was fourteen,’ commented Vesala.
The other five shortlisted books were a picture book for small children, Rakastunut krokotiili (‘Crocodile in love’, Tammi) by Hannu Hirvonen & Pia Sakki, a philosophical picture book about being different and courageous entitled Jättityttö ja Pirhonen (‘Giant girl and Pirhonen’, Tammi) by Hannele Huovi and Kristiina Louhi; a dystopic story set in the 2300s, Routasisarukset (‘Sisters of permafrost’, WSOY), by Eija Lappalainen & Anne Leinonen; a novel about the war experiences of an Ingrian family, Kaukana omalta maalta (‘Far away from homeland’, WSOY) by Sisko Latvus and an illustrated book about gods and myths of the world, Taivaallinen suurperhe (‘Extended heavenly family’, Otava) by Marjatta Levanto & Julia Vuori.
The prize, awarded by the Finnish Book Foundation on 23 November, is worth €30,000.
Finlandia Prize for Fiction 2011
1 December 2011 | In the news
 The winner of the Finlandia Prize for Fiction 2011, worth €30,000, is Rosa Liksom, for her novel Hytti no 6 (‘Compartment number 6’, WSOY): read translated extracts and an introduction of the author here on this page.
The winner of the Finlandia Prize for Fiction 2011, worth €30,000, is Rosa Liksom, for her novel Hytti no 6 (‘Compartment number 6’, WSOY): read translated extracts and an introduction of the author here on this page.
The prize was awarded on 1 December. The winner was selected by the theatre manager Pekka Milonoff from a shortlist of six.
‘Hytti nro 6 is an extraordinarily compact, poetic and multilayered description of a train journey through Russia. The main character, a girl, leaves Moscow for Siberia, sharing a compartment with a vodka-swilling murderer who tells hair-raising stories about his own life and about the ways of his country. – Liksom is a master of controlled exaggeration. With a couple of carefully chosen brushstrokes, a mini-story, she is able to conjure up an entire human destiny,’ Milonoff commented.
Author and artist Rosa Liksom (alias Anni Ylävaara, born 1958), has since 1985 written novels, short stories, children’s book, comics and plays. Her books have been translated into 16 languages.
Appointed by the Finnish Book Foundation, the prize jury (journalist and critic Hannu Marttila, journalist Tuula Ketonen and translator Kristiina Rikman) shortlisted the following novels: Kallorumpu (‘Skull drum’, Teos) by Eeva-Kaarina Aronen, William N. Päiväkirja (‘William N. Diary’, Otava) by Kristina Carlson, Huorasatu (‘Whore tale’, Into) by Laura Gustafsson, Minä, Katariina (‘I, Catherine’, Otava) by Laila Hirvisaari, and Isänmaan tähden (‘For fatherland’s sake’, first novel; Teos) by Jenni Linturi.
Rosa Liksom travelled a great deal in the Soviet Union in the 1980s. She said she hopes that literature, too, could play a role in promoting co-operation between people, cultures and nations: ‘For the time being there is no chance of some of us being able to live on a different planet.’
Government Prize for Translation 2011
24 November 2011 | In the news

María Martzoúkou. Photo: Charlotta Boucht
The Finnish Government Prize for Translation of Finnish Literature of 2011 – worth € 10,000 – was awarded to the Greek translator and linguist María Martzoúkou.
Martzoúkou (born 1958), who lives in Athens, where she works for the Finnish Institute, has studied Finnish language and literature as well as ancient Greek at the Helsinki University, where she has also taught modern Greek. She was the first Greek translator to publish translations of the Finnish epic, the Kalevala: the first edition, containing ten runes, appeared in 1992, the second, containing ten more, in 2004.
‘Saarikoski was the beginning,’ she says; she became interested in modern Finnish poetry, in particular in the poems of Pentti Saarikoski (1937–1983). As Saarikoski also translated Greek literature into Finnish, Martzoúkou found herself doubly interested in his works.
Later she has translated poetry by, among others, Tua Forsström, Paavo Haavikko, Riina Katajavuori, Arto Melleri, Annukka Peura, Pentti Saaritsa, Kirsti Simonsuuri and Caj Westerberg.
Among the Finnish novelists Martzoúkou has translated are Mika Waltari (five novels; the sixth, Turms kuolematon, The Etruscan, is in the printing press), Väinö Linna (Tuntematon sotilas, The Unknown Soldier) and Sofi Oksanen (Puhdistus, Purge).
María Martzoúkou received her award in Helsinki on 22 November from the minister of culture and sports, Paavo Arhinmäki. Thanking Martzoúkou for the work she has done for Finnish fiction, he pointed out that The Finnish Institute in Athens will soon publish a book entitled Kreikka ja Suomen talvisota (‘Greece and the Finnish Winter War’), a study of the relations of Finland and Greece and the news of the Winter War (1939–1940) in the Greek press, and it contains articles by Martzoúkou.
The prize has been awarded – now for the 37th time – by the Ministry of Education and Culture since 1975 on the basis of a recommendation from FILI – Finnish Literature Exchange.
Finlandia Prize for Non-Fiction 2011
24 November 2011 | In the news
 ‘Scientific, aesthetic, timely: the work is all of these. A work of non-fiction can be both precisely factual and emotional, full of both information and soul. A good non-fiction book will surprise. I did not expect to be enthused by lichens, their variety and colours,’ declared Professor Alf Reen in announcing the winner of this year’s Finlandia Prize for Non-Fiction on 17 November.
‘Scientific, aesthetic, timely: the work is all of these. A work of non-fiction can be both precisely factual and emotional, full of both information and soul. A good non-fiction book will surprise. I did not expect to be enthused by lichens, their variety and colours,’ declared Professor Alf Reen in announcing the winner of this year’s Finlandia Prize for Non-Fiction on 17 November.
The winning work is Suomen jäkäläopas (‘Guidebook of lichens in Finland’), edited by Soili Stenroos & Teuvo Ahti & Katileena Lohtander & Leena Myllys (The Botanical Museum / The Finnish Museum of Natural History). The prize is worth €30,000.
The other works on the shortlist of six were the following: Kustaa III ja suuri merisota. Taistelut Suomenlahdella 1788–1790 [(‘Gustav III and the great sea war. Battles in the Gulf of Finland 1788–1790’, John Nurminen Foundation), written by Raoul Johnsson, with an editorial board consisting of Maria Grönroos & Ilkka Karttunen &Tommi Jokivaara & Juhani Kaskeala & Erik Båsk; Unihiekkaa etsimässä. Ratkaisuja vauvan ja taaperon unipulmiin (‘In search of the sandman. Solutions to babies’ and toddlers’ sleep problems’ ) by Anna Keski-Rahkonen & Minna Nalbantoglu (Duodecim); Operaatio Hokki. Päämajan vaiettu kaukopartio (‘Operation Hokki. Headquarters’ silenced long-distance patrol’), an account of a long-distance patrol strike in eastern Karelia during the Continuation War in 1944, by Mikko Porvali (Atena); Trotski (‘Trotsky’, Gummerus; biography) by Christer Pursiainen; and Lintukuvauksen käsikirja (‘Handbook of bird photography’) by Markus Varesvuo & Jari Peltomäki & Bence Máté (Docendo).
Turd i’ your teeth
24 November 2011 | This 'n' that

Swearwords: universal language? Picture: Wikimedia
The title is a phrase by Shakespeare’s contemporary Ben Jonson, used in his plays.
In Japanese, swearwords are unknown. The worst thing you can say to a member of the African Xoxa tribe is ‘hlebeshako’, which roughly translates as ‘your mother’s ears’. ‘Swearing involves one or more of the following: filth, the forbidden and the sacred,’ says the American-born journalist and author Bill Bryson in his book Mother Tongue. The Story of the English Language (1990). It is a very entertaining and enlightening work full of interesting facts and peculiarities, many of them about a languages other than English.
There is one faulty reference to the Finnish language, though, and we do wonder how it has got into the book:
‘The Finns, lacking the sort of words you need to describe your feelings when you stub your toe getting up to answer a wrong number at 2.00 a.m., rather oddly adopted the word ravintolassa. It means “in the restaurant”.’ (p. 210)
Indeed it does, and definitely we never did. Adopt, that is. We’ve never ever heard anyone substituting a solid swearword – and there is no lack of sustainable, onomatopoeically effective (lots of r’s) examples in the Finnish language – for ‘ravintolassa’. Darn! Any Finn (prone to cursing) would say PERRRKELE, for example.
Someone, we fear, has been having Mr Bryson on.
